Version 1.1 (2016)
Tutorial
INDEX
REQUIREMENTS
SET UP
1. Creation of a local Gene eukaryotic entries database
1.1. Downloading the Gene eukaryotic entries
1.2. Parsing the Gene entries
1.3. Importing the Gene entries
2. Creation of a local exon and intron sequence database
2.1. Downloading and parsing the chromosome sequenses
2.2. Calculating exon and intron sequences
2.3. Importing exon and intron sequences
2.4. Exporting sequences in FASTA format
3. Additional tables
3.1. Transcripts table
3.2. Reports table
3.3. Genes table
GENERAL DEFINITIONS
4.1 File
4.2 Table
4.3 Record
4.4 Field
4.5 Layout
4.6 Browse Mode
4.7 Find Mode
4.8 Preview Mode
MENU AND COMMANDS
5.1 GeneBase
5.2 File
5.3 Edit
5.4 View
5.5 Records
5.6 Scripts
5.7 Help
TROUBLESHOOTING
REQUIREMENTS
(Back to Index)
The minimum
software requirements
are:
Mac OS X 10.6, OS X Lion 10.7, OS X Mountain Lion 10.8;
Windows XP Professional, Home Edition (Service Pack 3);
Windows Vista Ultimate, Business, Home Premium (Service Pack 2);
Windows 7 Ultimate, Professional, Home Premium;
Windows 8 Standard and Pro edition.
Minimum system requirements are:
Mac OS X 10.6, Intel-based Mac CPU (Central Processing Unit), 1 GigaByte (GB) of RAM (Random Access Memory), 1024x768 or higher resolution video adapter and display.
Windows XP Professional, Home Edition (Service Pack 3), 700 MegaHertz (MHz) CPU or faster, 256 MegaBytes (MB) of RAM, 1024x768 or higher resolution video adapter and display.
Mac OS X 10.6, OS X Lion 10.7, OS X Mountain Lion 10.8;
Windows XP Professional, Home Edition (Service Pack 3);
Windows Vista Ultimate, Business, Home Premium (Service Pack 2);
Windows 7 Ultimate, Professional, Home Premium;
Windows 8 Standard and Pro edition.
Minimum system requirements are:
Mac OS X 10.6, Intel-based Mac CPU (Central Processing Unit), 1 GigaByte (GB) of RAM (Random Access Memory), 1024x768 or higher resolution video adapter and display.
Windows XP Professional, Home Edition (Service Pack 3), 700 MegaHertz (MHz) CPU or faster, 256 MegaBytes (MB) of RAM, 1024x768 or higher resolution video adapter and display.
A connection to the Internet
is required to display the software Guide and to
download data for set up, but not to run the tool.
The downloaded file
should be automatically decompressed, generating a "GeneBase"
folder.
Failing this, double click on the file to activate the default decompression utility of your system.
Failing this, double click on the file to activate the default decompression utility of your system.
The
GeneBase Folder contains:
"GeneBase" (Macintosh) or "GeneBase.exe" (Windows) file
(the runtime application);
"GeneBase.fmp12" (database file);
"FMP Acknowledgments.pdf" file;
"Extensions" folder, containing a "Dictionaries" folder,
with the dictionary file for supported languages;
(and an "English" folder with 3 files, for Windows);
40 ".dll" files (for Windows);
"parse_entrezgene.py" file (only in the empty template version);
"calculate_sequences.py" file (only in the empty template version).
"GeneBase" (Macintosh) or "GeneBase.exe" (Windows) file
(the runtime application);
"GeneBase.fmp12" (database file);
"FMP Acknowledgments.pdf" file;
"Extensions" folder, containing a "Dictionaries" folder,
with the dictionary file for supported languages;
(and an "English" folder with 3 files, for Windows);
40 ".dll" files (for Windows);
"parse_entrezgene.py" file (only in the empty template version);
"calculate_sequences.py" file (only in the empty template version).
GeneBase
is based on FileMaker Pro 12 (FileMaker Pro, Inc.) database management
software (www.filemaker.com/index.html),
and is
released as a FileMaker Pro 12 template, along with a runtime
application able to run "FileMaker Pro" at the core of the
software.
The runtime is freely distributed, in compliance with the license of "FileMaker Pro 12 Advanced" developer package that was used to create the program.
The runtime is freely distributed, in compliance with the license of "FileMaker Pro 12 Advanced" developer package that was used to create the program.
Standard database commands (Find, Sort, Export
records) are available within each layout of GeneBase
(see "GENERAL DEFINITIONS"
and "MENU AND COMMANDS" sections in this
Guide).
Please do not change the names of any files and in the GeneBase folder.
Please do not change the names of any files and in the GeneBase folder.
NOTE - Be sure that
your system default format uses
"." (full stop)
as a decimal separator (English standard).
If this is not the case, you must change the system setting.
"." (full stop)
as a decimal separator (English standard).
If this is not the case, you must change the system setting.
Mac OS X: in
"System Preferences" (from the "Apple" Menu), click on
"International", then on "Formats", then choose as
"Region" a country with the English standard format for
numbers (full stop mark as a decimal separator).
System
restart or user logout is not required to make the
change effective.
Windows: in "Control Panel" (from the "Start" Menu), click on "International options" then modify the format of numbers choosing a country with the English standard format for numbers (full stop mark as a decimal separator).
System restart or user logout is not required to make the change effective.
Python 2.6 or 2.7 (https://www.python.org/) is only required to run the scripts useful for some set up steps.
Windows: in "Control Panel" (from the "Start" Menu), click on "International options" then modify the format of numbers choosing a country with the English standard format for numbers (full stop mark as a decimal separator).
System restart or user logout is not required to make the change effective.
Python 2.6 or 2.7 (https://www.python.org/) is only required to run the scripts useful for some set up steps.
1. Creation of a local Gene eukaryotic entries database
(Back to Index)
In this section, the user is guided to
download, parse and import the National Center for
Biotechnology Information's (NCBI) Gene database entries
into the GeneBase tables software.
Go to
the website page:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene
Using the Entrez text query, find the set of genes of interest.
Please note that if there are millions of resulting entries, in order to avoid downloading errors, it is highly recommended that you split them through different searches and subsequently download different files instead of one over-sized file.
As many Prokaryota lack a gene table listing the exon/intron structure and thus are not supported, please add to your search:
AND "eukaryota"[organism]
We also recommend you add the following restrictions, to avoid genes without a gene table structure (causing errors during parsing steps), by typing in the Search box:
AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[Properties]
These criteria selects for gene entries from a genomic source ("source_genomic"), current and primary and not obsolete ("alive"), and related to a known RefSeq reference sequence ("srcdb_refseq_known").
For further explanations, please see the Gene Help book
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK3841/)
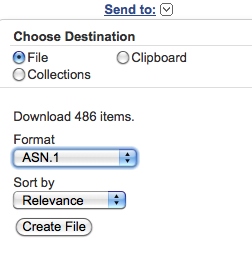
You can download the found entry set by selecting from the "Send to" pop-up menu at the top righthand corner of the web page:
"File", "Format ASN.1" and "Sort by Relevance"; then click on the "Create File" button.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene
Using the Entrez text query, find the set of genes of interest.
Please note that if there are millions of resulting entries, in order to avoid downloading errors, it is highly recommended that you split them through different searches and subsequently download different files instead of one over-sized file.
As many Prokaryota lack a gene table listing the exon/intron structure and thus are not supported, please add to your search:
AND "eukaryota"[organism]
We also recommend you add the following restrictions, to avoid genes without a gene table structure (causing errors during parsing steps), by typing in the Search box:
AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[Properties]
These criteria selects for gene entries from a genomic source ("source_genomic"), current and primary and not obsolete ("alive"), and related to a known RefSeq reference sequence ("srcdb_refseq_known").
For further explanations, please see the Gene Help book
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK3841/)
You can download the found entry set by selecting from the "Send to" pop-up menu at the top righthand corner of the web page:
"File", "Format ASN.1" and "Sort by Relevance"; then click on the "Create File" button.
In the default download
folder of your browser, you will obtain a file usually
named "gene_result.txt".
The download could take some hours, depending on the number and the size of retrieved genes.
Example 1
In order to obtain only current entries about genomic genes from the Animalia, Plants and Fungi kingdoms, excluding RefSeq models, download each kingdom set separately using the following representative queries:
"Animalia"[Organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
"Plants"[Organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
"Fungi"[Organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
In the default download folder of your browser, you will obtain three files usually named "gene_result.txt", "gene_result(1).txt" and "gene_result(2).txt". Please note that you need to have these files in the Genebase folder.
Example 2
In order to obtain only current entries about eukaryotic SOD1 genes, excluding RefSeq models, use the following representative query:
"SOD1"[Gene] AND "eukaryota"[organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
The download could take some hours, depending on the number and the size of retrieved genes.
Example 1
In order to obtain only current entries about genomic genes from the Animalia, Plants and Fungi kingdoms, excluding RefSeq models, download each kingdom set separately using the following representative queries:
"Animalia"[Organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
"Plants"[Organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
"Fungi"[Organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
In the default download folder of your browser, you will obtain three files usually named "gene_result.txt", "gene_result(1).txt" and "gene_result(2).txt". Please note that you need to have these files in the Genebase folder.
Example 2
In order to obtain only current entries about eukaryotic SOD1 genes, excluding RefSeq models, use the following representative query:
"SOD1"[Gene] AND "eukaryota"[organism] AND "source_genomic"[properties] AND alive[property] AND "srcdb_refseq_known"[properties]
1.2) Parsing the Gene entries
The "parse_entrezgene.py"
Python script provided here extracts and parses all
the available information contained in the
"gene_result.txt" file(s) and creates three tab-delimited
files that can be imported into the GeneBase software.
The "gene_result.txt" file(s) needs to be in the same directory from which the command is launched. Execute the program by typing the UNIX command "python parse_entrezgene.py" or by running the script from the IDLE utility.
For those not used to UNIX and Python languages, we recommend using the IDLE utility to run Python scripts provided here. Please see the following quick guide (Section A).
The programme is finished when the message "XXX gene results processed" appears, where XXX is the number of NCBI's Gene entries downloaded in the first step. In the working folder you will obtain three files "gene_ontology.txt", "gene_summary.txt" and gene_table.txt".
For the entire eukaryotic set, this step will require three hours.
The "gene_result.txt" file(s) needs to be in the same directory from which the command is launched. Execute the program by typing the UNIX command "python parse_entrezgene.py" or by running the script from the IDLE utility.
For those not used to UNIX and Python languages, we recommend using the IDLE utility to run Python scripts provided here. Please see the following quick guide (Section A).
The programme is finished when the message "XXX gene results processed" appears, where XXX is the number of NCBI's Gene entries downloaded in the first step. In the working folder you will obtain three files "gene_ontology.txt", "gene_summary.txt" and gene_table.txt".
For the entire eukaryotic set, this step will require three hours.
Copy (if
not already there) the "gene_ontology.txt", "gene_summary.txt"
and "gene_table.txt" files into the folder where an
empty copy of the GeneBase.fmp12 database is available. Open
the GeneBase database and import the three files selecting the script "Import_Summary_Table_Ontology" from the "Scripts"
menu.
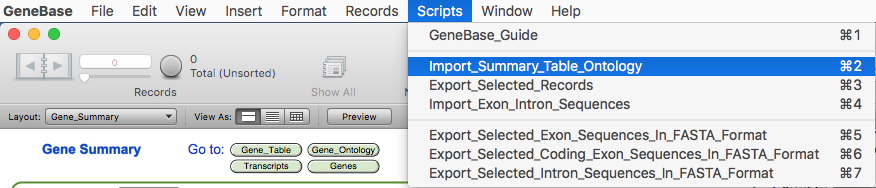
At the start of the import
process, the user needs to choose whether to retain or
delete all previously imported data. Clicking on "No" in
the first dialogue box will let the user add to the other
previously imported data records; otherwise, by clicking
on "Yes", all previously imported
data will be deleted and only new data will be
available.
A message will
appear warning that the import step is complete.
For the entire eukaryotic set, this step will require five days.
Now you can navigate between four different database tables containing the available information. The green buttons will help to navigate among software tables; the blue buttons will open useful external links about the gene or the gene product of the current record; the orange buttons will help to navigate between table records.
For the entire eukaryotic set, this step will require five days.
Now you can navigate between four different database tables containing the available information. The green buttons will help to navigate among software tables; the blue buttons will open useful external links about the gene or the gene product of the current record; the orange buttons will help to navigate between table records.
Gene_Summary and Gene_Table tables have a
box on the right, showing useful related fields of other
related software tables, giving the opportunity to perform
crossed searches.
Here
is the Gene_Summary table:
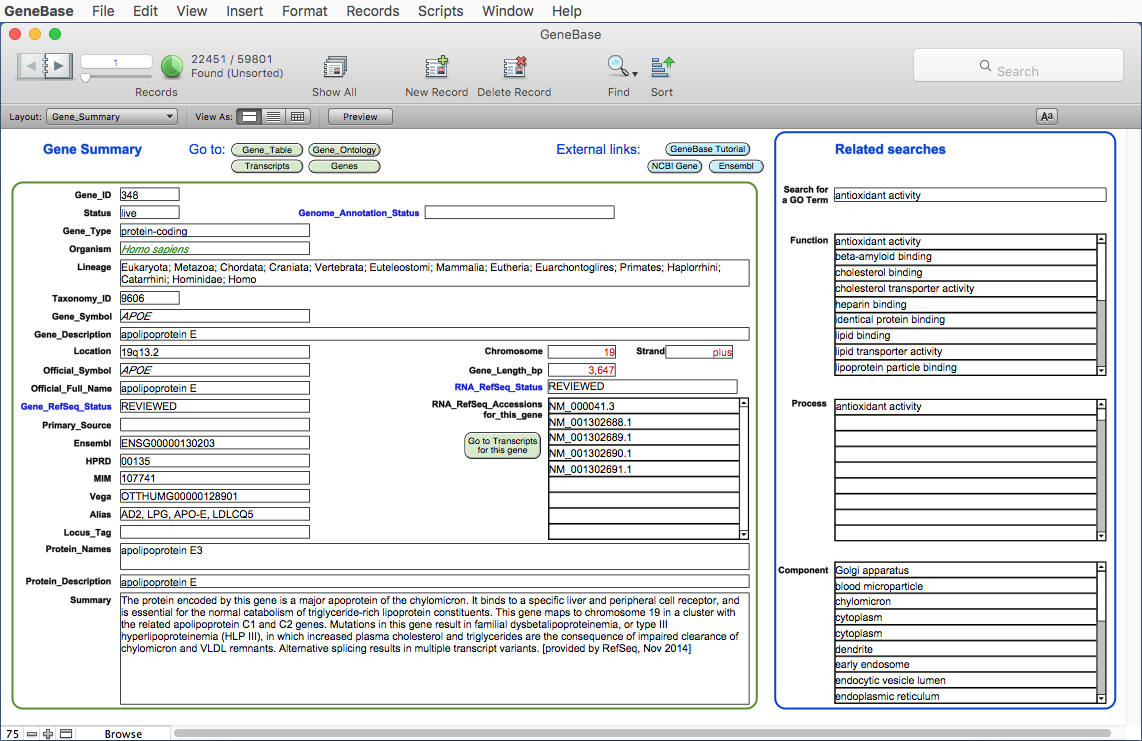
The software
will calculate and extract information for each gene in
specific calculated
fields of the Gene_Summary table:
FIELD
DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID":
the Entrez
gene unique identifier; for an efficient record
retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using this field
instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval
of genes with the same root);
"Status": the gene entry status;
"Genome_Annotation_Status": shows "not in current annotation release" if the gene is not
annotated on the most recent genome annotation (it may happen
also with "live" gene entries), otherwise is empty;
retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using this field
instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval
of genes with the same root);
"Status": the gene entry status;
"Genome_Annotation_Status": shows "not in current annotation release" if the gene is not
annotated on the most recent genome annotation (it may happen
also with "live" gene entries), otherwise is empty;
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA, snoRNA,
miscRNA, ncRNA, protein-coding, pseudo, other, and unknown;
(for an efficient record retrieval we recommend using
"protein coding" without the "-" symbol);
"Organism": the binomial organism's Latin name (Genus species) and strain
when appropriate;
"Lineage": the lineage;
"Taxonomy_ID": the NCBI Taxonomy database entry identifier;
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record retrieval we
recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol
(for example using the search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene
FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1);
"Gene_Description": the full descriptive name;
"Location": the genomic location of the gene;
"Official_Symbol": the gene symbol provided by the named external authority;
"Official_Full_Name": the gene's full name provided by the named external
authority;
"Gene_RefSeq_Status": any of the set of gene-level status descriptions defined by
RefSeq;
"Primary_Source": the identifier of the major resource outside of NCBI that
provided information about this gene. For some taxa, this
resource may be the nomenclature authority; in other taxa it
may be the group that defines genes and submits annotation to
public sequence databases;
"Ensembl": the matching Ensembl accession number;
"HPRD": the Human Protein Reference Database accession number (human
only);
"MIM": the Mendelian Inheritance in Man (MIM) number for the gene
(human only);
"Vega": the matching Vega (The Vertebrate Genome Annotation Database)
accession number;
"Alias": unofficial symbols and descriptions that have been used for
this gene and its products. If there is no official symbol,
and no locus_tag, the symbol at the top of the display is repeated in this section;
"Locus_Tag": corresponds to the systematic feature qualifier used by the
international sequence collaboration (INSDC, DDBJ/EMBL /GenBank) and can be assigned by sequence submitters as a
unique, systematic gene descriptor. When such a value is not available from the submitted sequence, the identifier from a
collaborating model organism database is used. Locus tag is also used as the preferred symbol if an official symbol has not been used to identify a gene;
"Protein_Names": the protein names as annotated on the RefSeq protein;
"Protein_Description": the protein descriptive text;
"Summary": descriptive text about the gene, its cellular localization, its function, and its effect on phenotype;
"Chromosome": the number of chromosome were the gene is located; shows X or
Y if gene is located in sex cromosomes;
"Gene_Length_bp": the length of the gene in base pair (bp);
"RNA_Refseq_Status": this field shows the RefSeq status of the reference
transcript associated with this gene;
"RNA_RefSeq_Accessions
for_this_gene": this field shows all the transcript accession numbers
associated with this gene; possible prefixs are: "NM" (RNA
messenger), "NR" (RNA), "XM" (RNA messenger, predicted
model), "XR" (RNA, predicted model); for further information
please see NCBI RefSeq; click on the green button Go to
Transcritps for this gene to show Transcripts records related
to the current gene.
Here is the Gene_Table table:
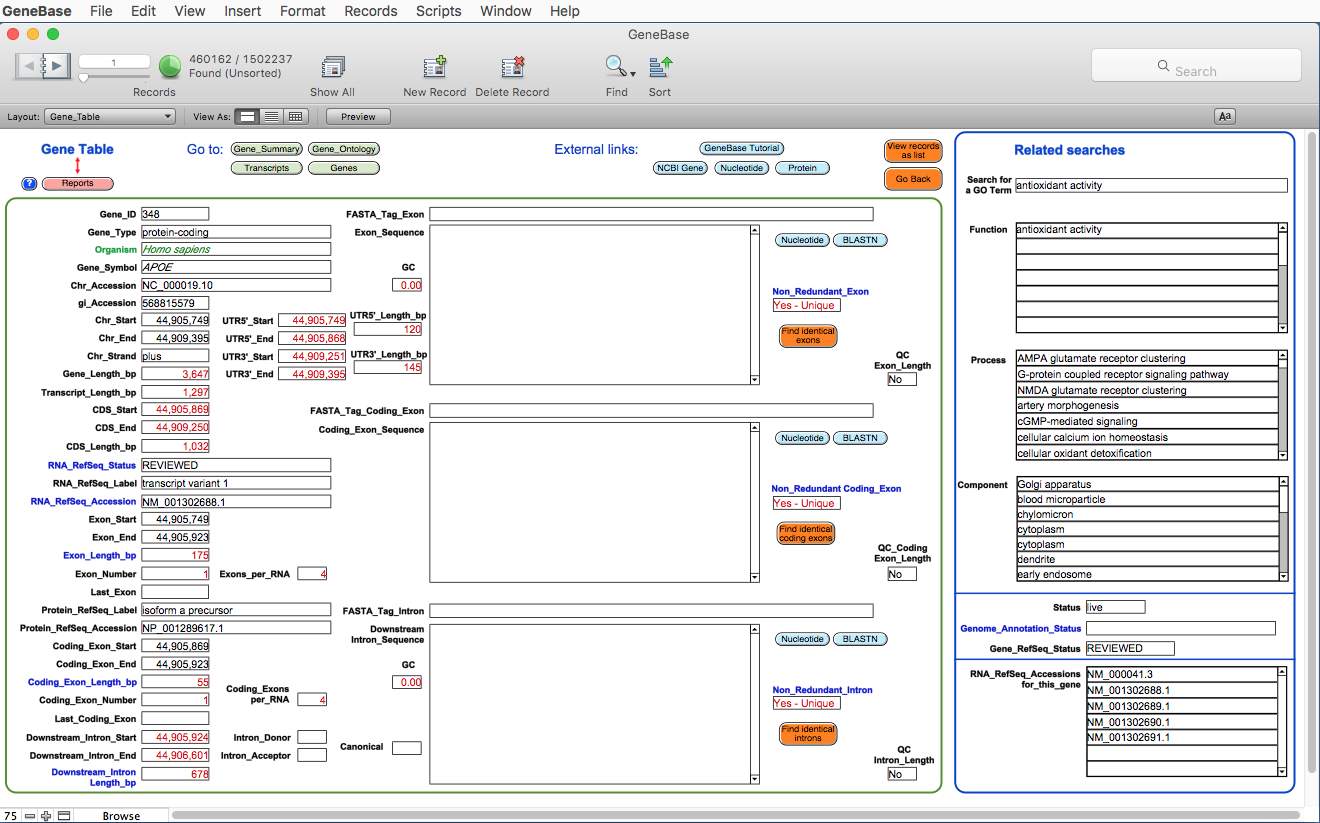
The
software has calculated and
extracted information for each available exon
(including the corresponding intron if an intron
follows that exon); useful numbers and information
specifically calculated by GeneBase and not available
in NCBI Gene are highlighted in red. Each record
represents one exon with the following calculated fields:
FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID": the Entrez gene unique identifier; for an
efficient record retrieval of unique gene/s we
recommend using this field instead of the gene
symbol (which may lead to the retrieval of genes
with the same root);
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA,
snoRNA, miscRNA, ncRNA, protein-coding, pseudo,
other, and unknown; (for an efficient record
retrieval we recommend using "protein coding"
without the "-" symbol); this property is
associated with the gene itself and not with the
transcript entries; the RNA type can be deduced
by the "RNA_RefSeq_Accession" (please see
below);
"Organism": the binomial organism's Latin name (Genus
species) and strain when appropriate;
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record
retrieval we recommend using the "=" symbol
followed by the gene symbol (for example using
the search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene FAS and
the antisense FAS-AS1);
"Chr_Accession": the chromosome entry GenBank accession number;
(for an efficient record retrieval we recommend
using for example "NC" without the "_" symbol);
"gi_Accession": the GenInfo identifier assigned to the
chromosome sequence;
"Chr_Start": the genomic coordinate of the gene start;
"Chr_End": the genomic coordinate of the gene end;
"Chr_Strand": shows "plus" or "minus" for genome strands
respectively;
"Gene_Length_bp": the length of the gene in base pair (bp);
"UTR5'_Start": the genomic coordinate of the 5´ untranslated
region start (UTR) (calculated only for protein
coding transcripts);
"UTR5'_End": the genomic coordinate of the 5´ UTR (calculated
only for protein coding transcripts);
"UTR5'_Length_bp": the 5´ UTR length in bp (calculated only for
protein coding transcripts);
"UTR3'_Start": the genomic coordinate of the 3´ UTR (calculated
only for protein coding transcripts);
"UTR3'_End": the genomic coordinate of the 3´ UTR (calculated only for protein coding transcripts);
"UTR3'_Length_bp": the 3´ UTR length in bp (calculated only for
protein coding transcripts);
"CDS_Start": the genomic coordinate of the coding sequence
start (if present);
"CDS_End": the genomic coordinate of the coding sequence
end (if present);
"CDS_Length_bp": the length of the coding sequence (if present)
in bp;
"RNA_RefSeq_Status": any of the set of status descriptions defined
by RefSeq for each transcript variant;
"RNA_RefSeq_Label": the transcript variant number (if present);
"RNA_RefSeq_Accession": the RNA RefSeq accession number; (for an
efficient record retrieval we recommend using
for example "NM" without the "_" symbol);
possible prefixs are: "NM" (RNA messenger),
"NR" (RNA), "XM" (RNA messenger, predicted
model), "XR" (RNA, predicted model); for further
information please see NCBI RefSeq;
"Exon_Start": the genomic coordinate of the exon start;
"Exon_End": the genomic coordinate of the exon end;
"Exon_Length_bp": the length of the exon in bp;
"Exon_Number": the exon number;
"Exons_per_RNA": the total number of exons of the transcript;
"Last_Exon": shows "Yes" if it is the 3´ terminal exon;
"Protein_RefSeq_Label": the isoform number (if present);
"Protein_RefSeq_Accession": the protein RefSeq accession number; (for an
efficient record retrieval we recommend using
for example "NP" without the "_" symbol);
"Coding_Exon_Start": the genomic coordinate of the coding exon
start;
"Coding_Exon_End": the genomic coordinate of the coding exon end;
"Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the length of the coding exon in bp;
"Coding_Exon_Number": the coding exon number;
"Last_Coding_Exon": shows "Yes" if it is the last coding exon;
"Downstream_Intron_Start": the genomic coordinate of the intron start;
"Downstream_Intron_End": the genomic coordinate of the intron end;
"Downstream_Intron_Length_bp": the length of the intron in bp;
"Intron_Donor"*: please see section 2;
"Intron_Acceptor"*: please see section 2;
"Canonical"*: please see section 2;
"FASTA_Tag_Exon"*: please see section 2;
"FASTA_Tag_Coding_Exon"*: please see section 2;
"FASTA_Tag_Intron"*: please see section 2;
"Exon_Sequence"*: please see section 2;
"Coding_Exon_Sequence"*: please see section 2;
"Downstream_Intron_Sequence"*: please see section 2;
"Non_Redundant_Exon": shows "Yes - Unique" if this exon is unique;
shows "Yes - Merged" if this exon is the first
one of each group of exons belonging to
transcript variants and thus present multiple
times in the database; to search for a non
redundant set of exons just type "Yes" in this
field in the "Find Mode";
"Non_Redundant_Coding_Exon": shows "Yes - Unique" if this coding exon is
unique; shows "Yes - Merged" if this coding exon
is the first one of each group of coding exons
belonging to transcript variants and thus
present multiple times in the database; to
search for a non redundant set of coding exons
just type "Yes" in this field in the "Find
Mode";
"Non_Redundant_Intron": shows "Yes - Unique" if this intron is unique;
shows "Yes - Merged" if this intron is the first
one of each group of introns belonging to
transcript variants and thus present multiple
times in the database; to search for a non
redundant set of introns just type "Yes" in this
field in the "Find Mode";
"QC_Exon_Length"*: please see section 2;
"QC_Coding_Exon_Length"*: please see section 2;
"QC_Intron_Length"*: please see section 2.
* These fields are filled by
executing the steps described in section 2.
The orange button View records as list will change the view mode showing all the records of that isoform as a list, from 5´ (top) to 3´ (down).
The orange buttons Find identical exons, Find identical coding exons and Find identical introns will find identical exons / introns belonging to transcript variants based on exon / intron genomic coordinates (only if the corresponding fields are not empty). A window showing the number of the retrieved records will appear. The user can navigate through the retrieved records which represents the identical exons / introns found. If an exon / intron is unique, the retrieved number of records will be equal to 1. If exon / intron genomic coordinate fields are empty, a window advising that there are no exon / intron to search for will appear.
Here is the Gene_Ontology table:
The orange button View records as list will change the view mode showing all the records of that isoform as a list, from 5´ (top) to 3´ (down).
The orange buttons Find identical exons, Find identical coding exons and Find identical introns will find identical exons / introns belonging to transcript variants based on exon / intron genomic coordinates (only if the corresponding fields are not empty). A window showing the number of the retrieved records will appear. The user can navigate through the retrieved records which represents the identical exons / introns found. If an exon / intron is unique, the retrieved number of records will be equal to 1. If exon / intron genomic coordinate fields are empty, a window advising that there are no exon / intron to search for will appear.
Here is the Gene_Ontology table:
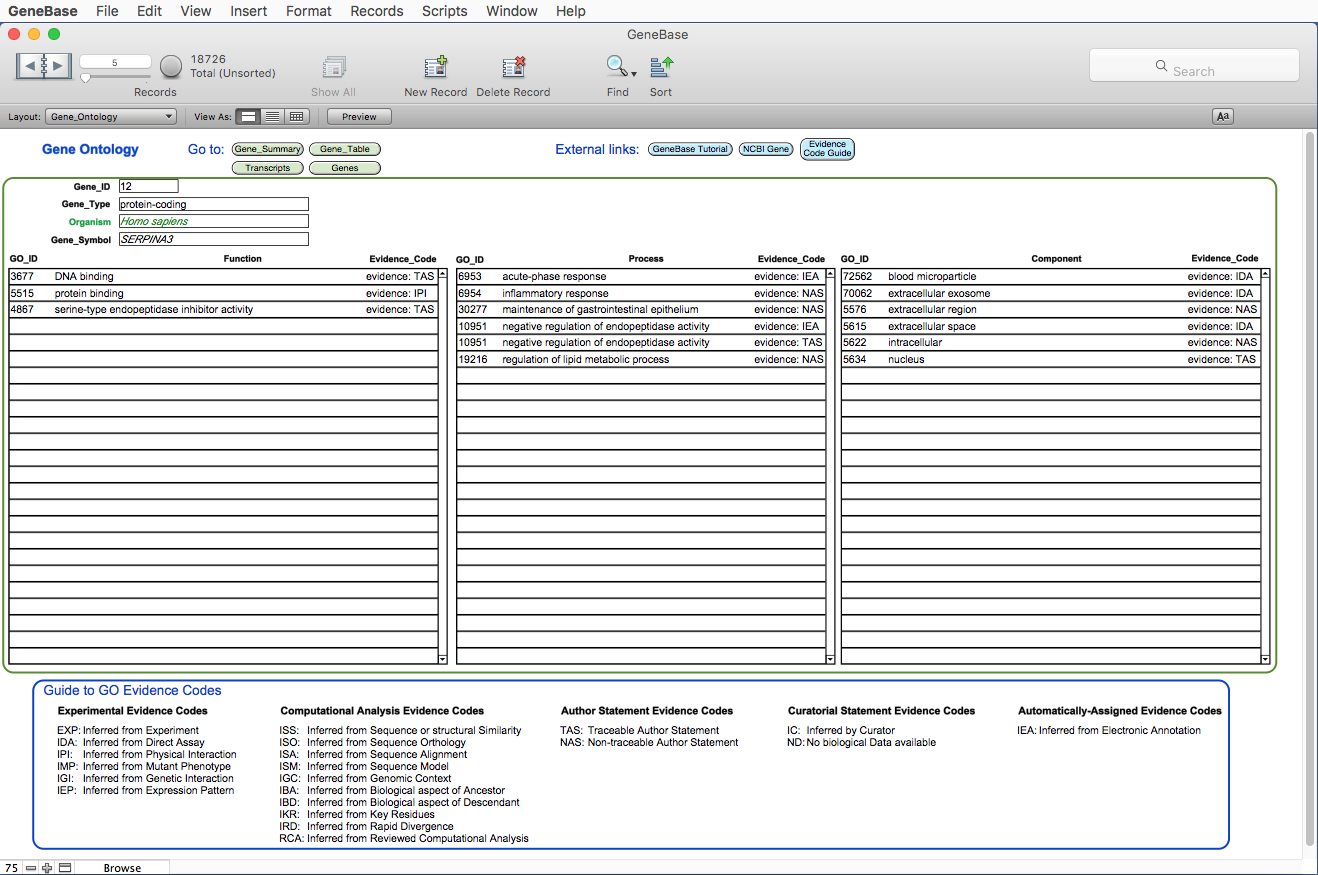
FIELDS DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID": the Entrez gene unique identifier; for an efficient record retrieval
of unique gene/s we recommend using this field instead of the gene
symbol (which may lead to the retrieval of genes with the same root);
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA, snoRNA, miscRNA, ncRNA,
protein-coding, pseudo, other, and unknown; (for an efficient data
retrieval we recommend using "protein coding" without the "-"
symbol);
"Organism": the binomial organism's Latin name (Genus species) and strain when
appropriate;
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record retrieval we recommend using
the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol (for example using the
search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1);
"GO_ID": the Gene Ontology (GO) identifier number (for example GO:51117);
"Evidence_Code": the Evidence information (explanations for these abbreviations are
provided by the Gene Ontology website: click on the blue button
"Evidence Code Guide").
2. Creation of a local exon and intron sequence database
(Back to Index)
The Gene_Table
table is designed to contain intron and exon sequences
(please see Gene_Table
field descriptions in section 1.3). In this section,
the user is guided to download and parse chromosome
sequences and to calculate exon and intron sequences to be
imported into GeneBase local database. The user can choose
a record subset from which to calculate sequences, for
example selecting only protein-coding genes.
2.1) Downloading and
parsing chromosome sequences
On the web page select:
Database: Nucleotide;
File: click on the "Browse" button and select the "chr_accession.txt" created
in the previous step and located in the GeneBase folder.
2.2)
Calculating
exon and intron sequences
2.3) Importing exon and intron sequences
FIELD DESCRIPTION
"QC_Coding_Exon_Length": shows "Yes" if the coding exon calculated sequence is of
the correct length (length stated in
"Coding_Exon_Length_bp" field), otherwise shows "No";
"QC_Intron_Length": shows "Yes" if the intron calculated sequence is of the
correct length (length stated in "Intron_Length_bp"
field), otherwise shows "No".
2.4) Exporting sequences in FASTA format
(Back to Index)
3.1) Transcripts table
FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID" the Entrez gene unique identifier; for an efficient record
retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using this field
instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval
of genes with the same root);
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record retrieval we
recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol
(for example using the search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene
FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1);
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA, snoRNA,
miscRNA, ncRNA, protein-coding, pseudo, other, and unknown;
this property is associated with the gene itself and not with
the transcript entries; the RNA type can be deduced by the
"RNA_RefSeq_Accession" (please see below);
"Gene_RefSeq_Status": any of the set of gene-level status descriptions defined by
RefSeq;
"RNA_Refseq_Status": any of the set of status descriptions defined by RefSeq for
each transcript variant;
"RNA_Refseq_Accession": the RNA RefSeq accession number; possible prefixs are: "NM"
(RNA messenger), "NR" (RNA), "XM" (RNA messenger, predicted
model), "XR" (RNA, predicted model); for further information
please see NCBI RefSeq;
"Transcript_Length_bp": shows the mature transcript (sum of all the exons) length in
bp; the "Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total"
values in bp of the transcript lengths for all the records
(or only for a set of found records) is shown at the bottom
of the page, in red fields;
"UTR5'_Length_bp": the 5´ UTR length in bp (calculated only for protein coding
transcripts); the "Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and
"Total" values in bp of the 5´ UTR lengths for all the records (or only for a set of found records) is shown at the bottom
of the page, in red fields;
"CDS_Length_bp": the length of the coding sequence (if present) in bp; the
"Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values in
bp of the CDS lengths for all the records (or only for a set
of found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"UTR3'_Length_bp": the 3´ UTR length in bp (calculated only for protein coding
transcripts); the "Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and
"Total" values in bp of the 3´ UTR lengths for all the
records (or only for a set of found records) is shown at the
bottom of the page, in red fields;
"Exons_per_RNA": the total number of exons of the transcript; the "Median",
"Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of the exon
number for all the records (or only for a set of found
records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red fields;
"Coding_Exons_per_RNA": the total number of coding exons of the transcript; the
"Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of
the exon number for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Genome_Annotation_Status": shows "not in current annotation release" if the gene is not
annotated on the most recent genome annotation (it may happen
also with "live" gene entries), otherwise is empty;
"Transcript_Count": this field is available only if records are sorted by
"Gene_ID" and for each gene will shows the number of
transcripts associated with that gene; please see sections
5.5 for details regarding "Sort" option of "Record Menu".
3.2) Reports table
FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Median_Exon_Length_bp": the median value of the length in bp of all
exons depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Mean_Exon_Length_bp": the mean value of the length in bp of all
exons depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Standard_Deviation_Exon_Length_bp": the standard deviation value of the length in
bp of all exons depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Total_Exon_Length_bp": the sum in bp of all exon lengths
depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Median_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the median value of the length in bp of all
coding exons depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Mean_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the mean value of the length in bp of all
coding exons depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Standard_Deviation_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the standard deviation value of the length in
bp of all coding exons depending on record
subsets found in Gene_Table;
"Total_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the sum in bp of all coding exon lengths
depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Median_Intron_Length_bp": the median value of the length in bp of all
introns depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Mean_Intron_Length_bp": the mean value of the length in bp of all
introns depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Standard_Deviation_Intron_Length_bp": the standard deviation value of the length in
bp of all introns depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Total_Intron_Length_bp": the sum in bp of all intron lengths depending
on record subsets found in Gene_Table.
3.3) Genes table
FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID" the Entrez gene unique identifier; for an efficient record
retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using this field
instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval
of genes with the same root);
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record retrieval we
recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol
(for example using the search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene
FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1);
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA, snoRNA,
miscRNA, ncRNA, protein-coding, pseudo, other, and unknown;
"Gene_RefSeq_Status": any of the set of gene-level status descriptions defined by
RefSeq;
"RNA_Refseq_Status": this field shows the RefSeq status of the reference
transcript associated with this gene;
"Gene_Length_bp": shows the gene length in bp; the "Median", "Mean",
"Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values in bp of the
transcript lengths for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Transcripts_per_Gene": the total number of transcripts of the gene; the "Median",
"Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of the
transcript number for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Exons_per_RNA": the total number of exons of the transcript; the "Median",
"Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of the exon
number for all the records (or only for a set of found
records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red fields;
"Coding_Exons_per_RNA": the total number of coding exons of the transcript; the
"Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of
the exon number for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Genome_Annotation_Status": shows "not in current annotation release" if the gene is not
annotated on the most recent genome annotation (it may happen
also with "live" gene entries), otherwise is empty.
From the Gene_Table
table select "Show all"
if you are interested in all available gene exons and
introns. Alternatively, the user can select a record subset from
which to calculate exon and intron sequences; please see sections 4 and
5 for
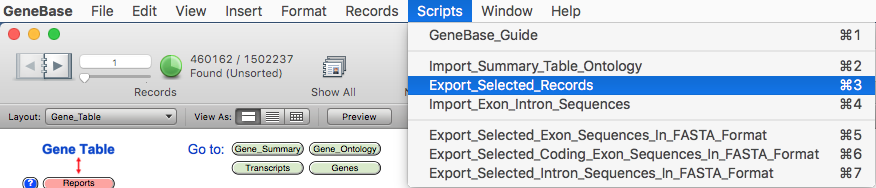
details regarding "Find Mode". Please select the script "Export_Selected_Records" from the
"Scripts" menu.

A
message will appear warning that the import step is
complete. The final output is the creation of two text
files in the GeneBase folder: one with the chromosome
accessions list (named "chr_accession.txt")
and one with exon and intron genomic coordinates (named
"exon_intron.txt"
and used in section 2.3);
both are related to all shown records or to the record
subset (depending on what the user is interested in).
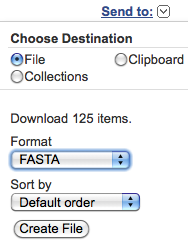
To download
chromosome sequences listed in the file named "chr_accession.txt"
go to the website page:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/batchentrez
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/batchentrez
On the web page select:
Database: Nucleotide;
File: click on the "Browse" button and select the "chr_accession.txt" created
in the previous step and located in the GeneBase folder.

By clicking on the "Retrieve" button, a window with
the description of the retrieved records will appear.
Click on the "Retrieve
records for XXX UID(s)" link (where XXX is
the number of the retrieved records that should be
equal to the number of chromosome accessions listed in
the uploaded file). You can download the found entry set
choosing from the "Send to" pop-up menu at the
right-top corner of the web page:
"File", "FASTA" and "Default Order"; then clicking on the "Create File" button.
"File", "FASTA" and "Default Order"; then clicking on the "Create File" button.

The download could
take some hours, depending on the number and the
size of chromosomes.
Please note that you should not exceed the download limit of 10 GB to avoid errors in the output file. You can divide the chromosome accession list file (chr_accession.txt) into two or more files and repeat the download step for each of them.
In the default download folder of your browser, you will obtain one or more files usually named "sequence.fasta", "sequence(1).fasta", "sequence(2).fasta" and so forth.
We recommend checking that the number of downloaded entries is equal to initial retrieved chromosome accession number (e.g. using the "grep" and "wc" UNIX utilities: grep gi sequence.fasta | wc -l).
Create a text file named exactly "file_list.txt" with a list of the downloaded FASTA file names (one row each name, even if you have only one file with the chromosome sequences, write only that name).
Example
If you have only one file with the chromosome sequences, write only: sequence.fasta.
If you have three files with the chromosome sequences, write:
sequence.fasta
sequence(1).fasta
sequence(2).fasta
For Windows users only: you need to convert the FASTA file(s) in tabular format, for example by using Galaxy web tool.
Please note that you should not exceed the download limit of 10 GB to avoid errors in the output file. You can divide the chromosome accession list file (chr_accession.txt) into two or more files and repeat the download step for each of them.
In the default download folder of your browser, you will obtain one or more files usually named "sequence.fasta", "sequence(1).fasta", "sequence(2).fasta" and so forth.
We recommend checking that the number of downloaded entries is equal to initial retrieved chromosome accession number (e.g. using the "grep" and "wc" UNIX utilities: grep gi sequence.fasta | wc -l).
Create a text file named exactly "file_list.txt" with a list of the downloaded FASTA file names (one row each name, even if you have only one file with the chromosome sequences, write only that name).
Example
If you have only one file with the chromosome sequences, write only: sequence.fasta.
If you have three files with the chromosome sequences, write:
sequence.fasta
sequence(1).fasta
sequence(2).fasta
For Windows users only: you need to convert the FASTA file(s) in tabular format, for example by using Galaxy web tool.
The "calculate_sequences.py" Python script
provided here automatically parses downloaded
chromosome sequences and extracts exon and intron
sequences using the genomic coordinates exported from
all or selected records of Gene_Table
database table (please see section 2.1).
You need to have the following files in the same folder:
1) the "calculate_sequences.py" script;
2) the "exon_intron.txt" file, containing the genomic coordinates and created in
section 2.1;
3) the FASTA file(s) with the chromosome sequences downloaded in section 2.1;
4) the text file "file_list.txt" with the list of the downloaded FASTA file names created in section 2.1.
Execute the "calculate_sequences.py" script by typing the UNIX command "python calculate_sequences.py" or by running the script from the IDLE utility.
For those not used to UNIX and Python languages, we recommend using the IDLE utility to run Python scripts provided here. Please see the following quick guide (Section B).
The programme is finished when the message "Exon and intron sequences calculated" appears. In the working folder you will obtain a file named "exon_intron_seq.tab".
For the "Validated" and "Reviewed" eukatyotic gene set, this step will require three hours.
You need to have the following files in the same folder:
1) the "calculate_sequences.py" script;
2) the "exon_intron.txt" file, containing the genomic coordinates and created in
section 2.1;
3) the FASTA file(s) with the chromosome sequences downloaded in section 2.1;
4) the text file "file_list.txt" with the list of the downloaded FASTA file names created in section 2.1.
Execute the "calculate_sequences.py" script by typing the UNIX command "python calculate_sequences.py" or by running the script from the IDLE utility.
For those not used to UNIX and Python languages, we recommend using the IDLE utility to run Python scripts provided here. Please see the following quick guide (Section B).
The programme is finished when the message "Exon and intron sequences calculated" appears. In the working folder you will obtain a file named "exon_intron_seq.tab".
For the "Validated" and "Reviewed" eukatyotic gene set, this step will require three hours.
2.3) Importing exon and intron sequences
If the file created
in the previous step ("exon_intron_seq.tab")
exceeds the size of 4 GB, please divide it in order
to create more files of less than 4 GB,
which is the size limit of text files to be imported
into a FileMaker database. Please repeat for each
file created
the following import step.
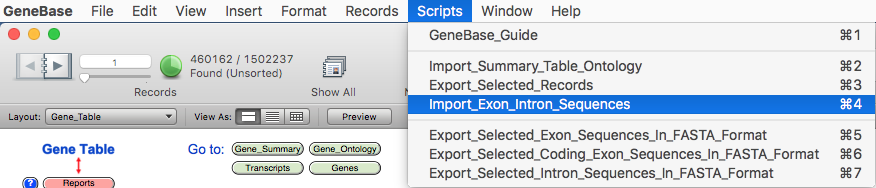
Import the exon and intron calculated sequences by selecting the script "Import_Exon_Intron_Sequences" from the GeneBase "Scripts" menu: a window will appear to find the sequence file(s) ("exon_intron_seq.tab") location.
Import the exon and intron calculated sequences by selecting the script "Import_Exon_Intron_Sequences" from the GeneBase "Scripts" menu: a window will appear to find the sequence file(s) ("exon_intron_seq.tab") location.

A
message will appear warning that the import step is
complete.
For the entire eukaryotic gene set, this step will require two days.
For the entire eukaryotic gene set, this step will require two days.
The software will
calculate and extract sequences and other information
in specific calculated fields of the Gene_Table
table:
FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Intron_Donor":
the intron donor site (5'
end);
"Intron_Acceptor": the intron acceptor site (3' end);
"Canonical": shows "Yes" if the donor site is "GT" and the acceptor
site is "AG", otherwise shows "No";
"FASTA_Tag_Exon"*: it shows the single-line identifier beginning with the ">"
symbol of the current exon sequence;
"FASTA_Tag_Coding_Exon"*: it shows the single-line identifier beginning with the ">"
symbol of the current coding exon sequence;
"FASTA_Tag_Intron"*: it shows the single-line identifier beginning with the ">"
symbol of the current intron sequence;
"Exon_Sequence": the exon sequence (each row has 50 bases); in order to
search for exact text at the end of the string, we
recommend the use of the * symbol, followed by the letters
(for example using the search "*CAG" will retrieve records
with exon sequence ending with "CAG");
"Coding_Exon_Sequence": the coding exon sequence (each row has 50 bases); in order
to search for exact text at the end of the string, we
recommend the use of the * symbol, followed by the letters
(for example using the search "*CAG" will retrieve records
with exon sequence ending with "CAG");
"Downstrean_Intron_Sequence": the intron sequence (each row has 50 bases); in order to
search for exact text at the end of the string, we
recommend the use of the * symbol, followed by the letters
(for example using the search "*CAG" will retrieve records
with intron sequence ending with "CAG");
"Intron_Acceptor": the intron acceptor site (3' end);
"Canonical": shows "Yes" if the donor site is "GT" and the acceptor
site is "AG", otherwise shows "No";
"FASTA_Tag_Exon"*: it shows the single-line identifier beginning with the ">"
symbol of the current exon sequence;
"FASTA_Tag_Coding_Exon"*: it shows the single-line identifier beginning with the ">"
symbol of the current coding exon sequence;
"FASTA_Tag_Intron"*: it shows the single-line identifier beginning with the ">"
symbol of the current intron sequence;
"Exon_Sequence": the exon sequence (each row has 50 bases); in order to
search for exact text at the end of the string, we
recommend the use of the * symbol, followed by the letters
(for example using the search "*CAG" will retrieve records
with exon sequence ending with "CAG");
"Coding_Exon_Sequence": the coding exon sequence (each row has 50 bases); in order
to search for exact text at the end of the string, we
recommend the use of the * symbol, followed by the letters
(for example using the search "*CAG" will retrieve records
with exon sequence ending with "CAG");
"Downstrean_Intron_Sequence": the intron sequence (each row has 50 bases); in order to
search for exact text at the end of the string, we
recommend the use of the * symbol, followed by the letters
(for example using the search "*CAG" will retrieve records
with intron sequence ending with "CAG");
"QC_Exon_Length":
shows "Yes"
if the exon calculated sequence is of the
correct length (length stated in "Exon_Length_bp" field),
otherwise shows "No";
correct length (length stated in "Exon_Length_bp" field),
otherwise shows "No";
"QC_Coding_Exon_Length": shows "Yes" if the coding exon calculated sequence is of
the correct length (length stated in
"Coding_Exon_Length_bp" field), otherwise shows "No";
"QC_Intron_Length": shows "Yes" if the intron calculated sequence is of the
correct length (length stated in "Intron_Length_bp"
field), otherwise shows "No".
2.4) Exporting sequences in FASTA format
From the Gene_Table
table select "Show all"
if you are interested in all available gene exons and
introns. Alternatively, the user can select a record subset from
which to export exon and intron sequences in FASTA
format. The omission
of records with empty "Exon_Sequence",
"Coding_Exon_Sequence"
or "Intron_Sequence"
fields is recommended, in order to speed up the
exporting step. Please see sections
4
and 5
for details regarding "Find Mode". The
set of current exon/coding exon/intron sequences can be
automatically exported in FASTA format by selecting, from the GeneBase "Scripts" menu,
the corresponding scripts:
"Export_Exon_Sequences_In_FASTA_Format", "Export_Coding_Exon_
Sequences_In_FASTA_Format" and "Export_Intron_Sequences_In_FASTA_Format".
A message will appear warning that each selected export step is complete. These scripts could take some hours and the database file size could temporarily increase, depending on the number and the size of sequences to be exported. The final output is the creation of a FASTA file in the GeneBase folder for each desired set: "Exons_FASTA.txt" and/or "Coding_Exons_FASTA.txt" and/or "Introns_FASTA.txt". These files contain the single-line identifiers (as indicated by the "Tag_Exon", "Tag_Coding_Exon" and "Tag_Intron" Gene_Table fields) and the corresponding sequences and are suitable, for example, for the creation of a local BLASTN database through the "makeblastbd" executable available along with the BLAST local suite.
Briefly, the user needs to install the operating system specific BLAST Command Line Applications from the following website page:
ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/LATEST/
The following example command line creates a BLAST local database from the exon sequences exported from GeneBase ("Exons_FASTA.txt"):
$ makeblastdb -in Exons_FASTA.txt -dbtype nucl -out Exons_db
Please note that merging at text level Exons_FASTA.txt and Intron_FASTA.txt files and processing this merged file with megablastdb would result in a complete exon/intron database.
The following example command line compares a file containing query sequences to the created local database:
$ blastn -query Query.txt -db Exons_db -out Results.txt
3.
Additional tablesSequences_In_FASTA_Format" and "Export_Intron_Sequences_In_FASTA_Format".
A message will appear warning that each selected export step is complete. These scripts could take some hours and the database file size could temporarily increase, depending on the number and the size of sequences to be exported. The final output is the creation of a FASTA file in the GeneBase folder for each desired set: "Exons_FASTA.txt" and/or "Coding_Exons_FASTA.txt" and/or "Introns_FASTA.txt". These files contain the single-line identifiers (as indicated by the "Tag_Exon", "Tag_Coding_Exon" and "Tag_Intron" Gene_Table fields) and the corresponding sequences and are suitable, for example, for the creation of a local BLASTN database through the "makeblastbd" executable available along with the BLAST local suite.
Briefly, the user needs to install the operating system specific BLAST Command Line Applications from the following website page:
ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/executables/blast+/LATEST/
The following example command line creates a BLAST local database from the exon sequences exported from GeneBase ("Exons_FASTA.txt"):
$ makeblastdb -in Exons_FASTA.txt -dbtype nucl -out Exons_db
Please note that merging at text level Exons_FASTA.txt and Intron_FASTA.txt files and processing this merged file with megablastdb would result in a complete exon/intron database.
The following example command line compares a file containing query sequences to the created local database:
$ blastn -query Query.txt -db Exons_db -out Results.txt
(Back to Index)
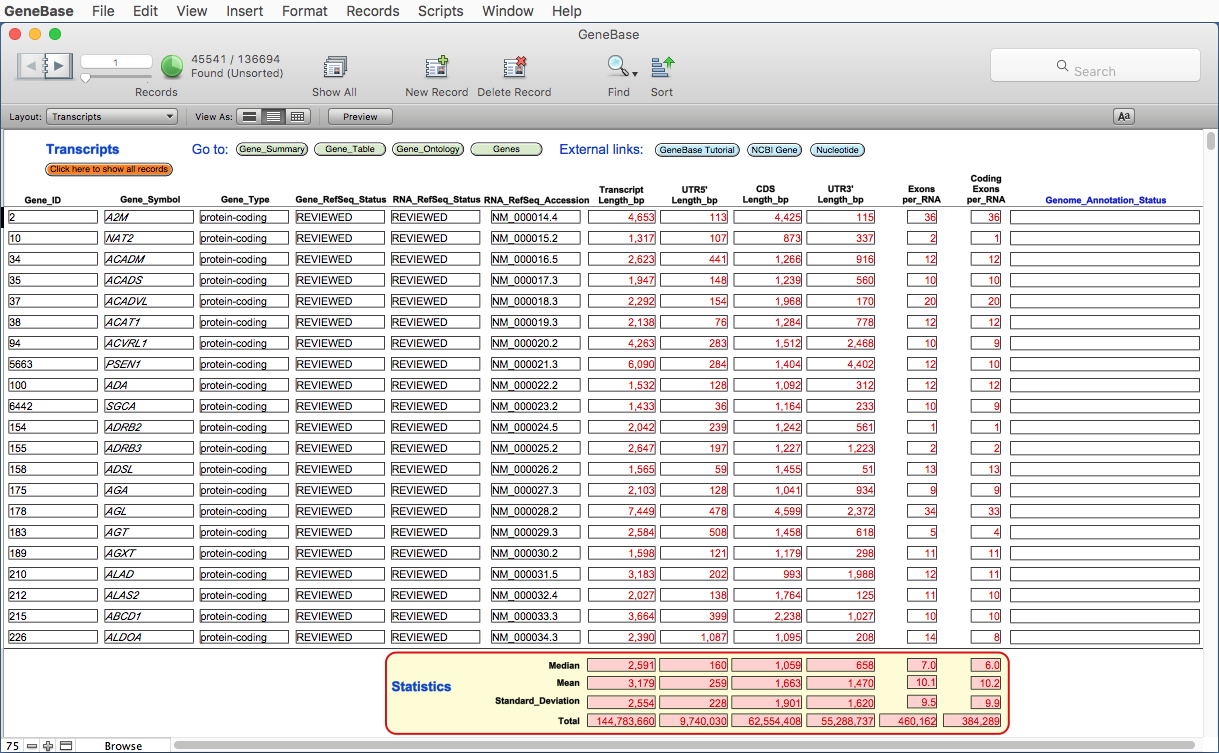
3.1) Transcripts table
A table named Transcripts
shows a set of useful fields from Gene_Summary and Gene_Table tables, in
order to give an overview of main available
information for each transcript.
This table will show dynamic summary fields for the current subset of records found.
Click on the orange button Click here to show all records to calculate statistics for all the records present in this table.
This table will show dynamic summary fields for the current subset of records found.
Click on the orange button Click here to show all records to calculate statistics for all the records present in this table.

FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID" the Entrez gene unique identifier; for an efficient record
retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using this field
instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval
of genes with the same root);
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record retrieval we
recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol
(for example using the search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene
FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1);
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA, snoRNA,
miscRNA, ncRNA, protein-coding, pseudo, other, and unknown;
this property is associated with the gene itself and not with
the transcript entries; the RNA type can be deduced by the
"RNA_RefSeq_Accession" (please see below);
"Gene_RefSeq_Status": any of the set of gene-level status descriptions defined by
RefSeq;
"RNA_Refseq_Status": any of the set of status descriptions defined by RefSeq for
each transcript variant;
"RNA_Refseq_Accession": the RNA RefSeq accession number; possible prefixs are: "NM"
(RNA messenger), "NR" (RNA), "XM" (RNA messenger, predicted
model), "XR" (RNA, predicted model); for further information
please see NCBI RefSeq;
"Transcript_Length_bp": shows the mature transcript (sum of all the exons) length in
bp; the "Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total"
values in bp of the transcript lengths for all the records
(or only for a set of found records) is shown at the bottom
of the page, in red fields;
"UTR5'_Length_bp": the 5´ UTR length in bp (calculated only for protein coding
transcripts); the "Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and
"Total" values in bp of the 5´ UTR lengths for all the records (or only for a set of found records) is shown at the bottom
of the page, in red fields;
"CDS_Length_bp": the length of the coding sequence (if present) in bp; the
"Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values in
bp of the CDS lengths for all the records (or only for a set
of found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"UTR3'_Length_bp": the 3´ UTR length in bp (calculated only for protein coding
transcripts); the "Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and
"Total" values in bp of the 3´ UTR lengths for all the
records (or only for a set of found records) is shown at the
bottom of the page, in red fields;
"Exons_per_RNA": the total number of exons of the transcript; the "Median",
"Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of the exon
number for all the records (or only for a set of found
records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red fields;
"Coding_Exons_per_RNA": the total number of coding exons of the transcript; the
"Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of
the exon number for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Genome_Annotation_Status": shows "not in current annotation release" if the gene is not
annotated on the most recent genome annotation (it may happen
also with "live" gene entries), otherwise is empty;
"Transcript_Count": this field is available only if records are sorted by
"Gene_ID" and for each gene will shows the number of
transcripts associated with that gene; please see sections
5.5 for details regarding "Sort" option of "Record Menu".
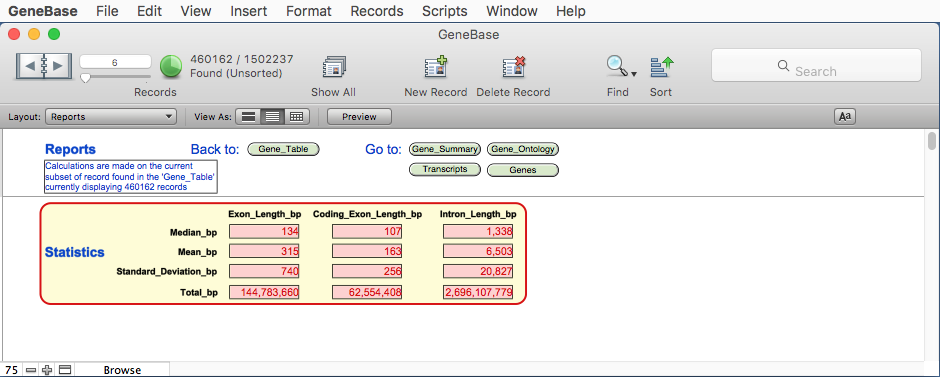
3.2) Reports table
In addition a fifth
table named Reports
is generated in order to calculate values of interest
for statistics. Values are updated depending on record
subsets found in Gene_Table:
for example, if you search for Gene_Table
records belonging to Homo sapiens (please see sections 4 and 5
for details regarding "Find Mode"), switching to the Reports
table, values will be updated considering the Homo sapiens
record subset. On the contrary, if you select "Show all" from the
Gene_Table
table, Reports
values will be calculated considering all available
records.
Depending on how many records are found, the calculations may take some time.
Depending on how many records are found, the calculations may take some time.

FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Median_Exon_Length_bp": the median value of the length in bp of all
exons depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Mean_Exon_Length_bp": the mean value of the length in bp of all
exons depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Standard_Deviation_Exon_Length_bp": the standard deviation value of the length in
bp of all exons depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Total_Exon_Length_bp": the sum in bp of all exon lengths
depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Median_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the median value of the length in bp of all
coding exons depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Mean_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the mean value of the length in bp of all
coding exons depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Standard_Deviation_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the standard deviation value of the length in
bp of all coding exons depending on record
subsets found in Gene_Table;
"Total_Coding_Exon_Length_bp": the sum in bp of all coding exon lengths
depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Median_Intron_Length_bp": the median value of the length in bp of all
introns depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Mean_Intron_Length_bp": the mean value of the length in bp of all
introns depending on record subsets found in
Gene_Table;
"Standard_Deviation_Intron_Length_bp": the standard deviation value of the length in
bp of all introns depending on record subsets
found in Gene_Table;
"Total_Intron_Length_bp": the sum in bp of all intron lengths depending
on record subsets found in Gene_Table.
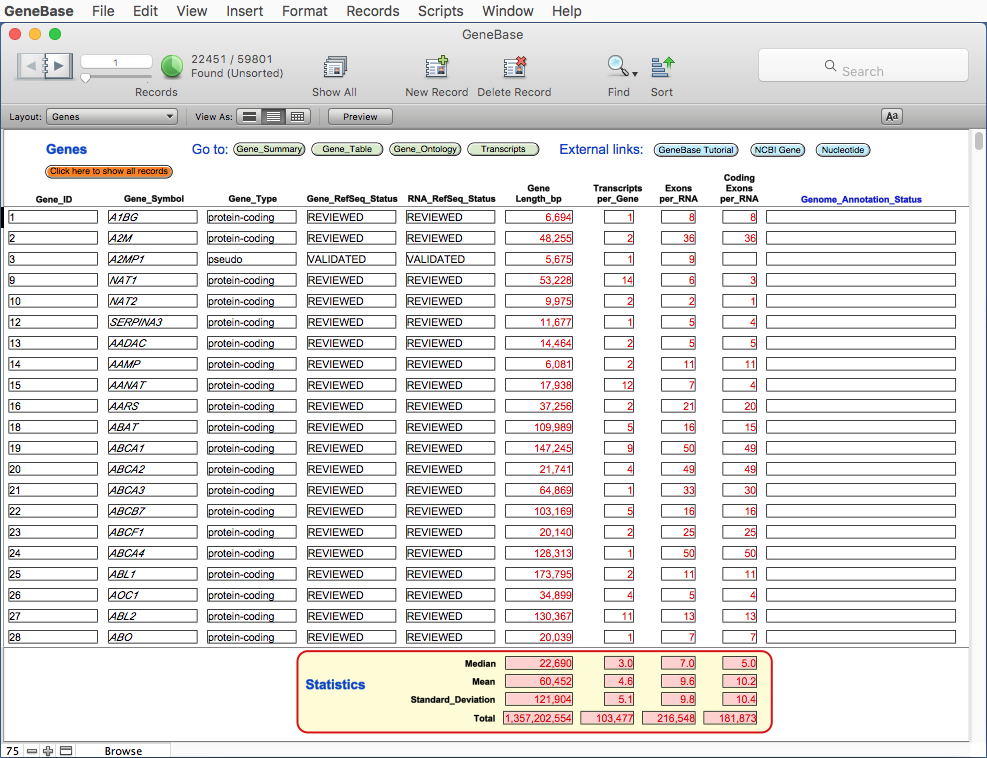
3.3) Genes table
A table named Genes shows a set of
useful fields from Gene_Summary
and Gene_Table
tables, in order to give an overview of main available
information for each gene. Here only the transcript
isoform with the highest number of exons is
arbitrarily shown for each gene.
This table will show dynamic summary fields for the current subset of records found.
Click on the orange button Click here to show all records to calculate statistics for all the records present in this table.
This table will show dynamic summary fields for the current subset of records found.
Click on the orange button Click here to show all records to calculate statistics for all the records present in this table.

FIELD DESCRIPTION
"Gene_ID" the Entrez gene unique identifier; for an efficient record
retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using this field
instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval
of genes with the same root);
"Gene_Symbol": the gene symbol; for an efficient record retrieval we
recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol
(for example using the search "=FAS" will retrieve the gene
FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1);
"Gene_Type": possible values are tRNA, rRNA, snRNA, scRNA, snoRNA,
miscRNA, ncRNA, protein-coding, pseudo, other, and unknown;
"Gene_RefSeq_Status": any of the set of gene-level status descriptions defined by
RefSeq;
"RNA_Refseq_Status": this field shows the RefSeq status of the reference
transcript associated with this gene;
"Gene_Length_bp": shows the gene length in bp; the "Median", "Mean",
"Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values in bp of the
transcript lengths for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Transcripts_per_Gene": the total number of transcripts of the gene; the "Median",
"Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of the
transcript number for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Exons_per_RNA": the total number of exons of the transcript; the "Median",
"Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of the exon
number for all the records (or only for a set of found
records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red fields;
"Coding_Exons_per_RNA": the total number of coding exons of the transcript; the
"Median", "Mean", "Standard_Deviation" and "Total" values of
the exon number for all the records (or only for a set of
found records) is shown at the bottom of the page, in red
fields;
"Genome_Annotation_Status": shows "not in current annotation release" if the gene is not
annotated on the most recent genome annotation (it may happen
also with "live" gene entries), otherwise is empty.
GeneBase contains now
information and sequences of genes of interest. Using general
FileMaker commands (please see following sections), the user
can perform original calculations and searches.
4. GENERAL DEFINITIONS
(Back to Index)
A set of records referring to
the same subject type (e.g., the Gene_Summary
table).
One set of
fields which represents one entry (i.e. containing all requested
data for a subject, e.g. a gene probe).
The record browser is a small book icon at the top left of the window.

You may also browse the records faster using the cursor to the right of the small book icon.
The record browser is a small book icon at the top left of the window.
You may also browse the records faster using the cursor to the right of the small book icon.
A particular graphical
organization of the field of a table.
A table can be visualized in more than one layout.
A layout may display fields from a table or its related fields from other tables.
A file may show data within different layouts.
Visualization of a field is independent from the storage of the contained data.
Browsing among the layouts can be done by clicking on the 'Layout:' pop-up Menu in the upper left corner.
You may browse the database by clicking on the small book pages at the top left of the window, by using the cursor to the right of the small book icon or by
entering a record number and clicking on the "Return" key.
The following information is constantly displayed on the Status toolbar (if not, select "Status Toolbar" from the "View" Menu):
Records: total number of Records in the table.
Found: total number of the subset of Records currently selected. Clicking on the green circular button will retrieve the complementary subset of currently omitted records.
Sorted: sorting status of the Records (Sorted/Unsorted).
The FileMaker Pro-based database may be used basically in these "modes":
'Browse', 'Find', and 'Preview'.
Switching among different modes can be done from the 'View' Menu or from the pop-up Menu bar at the bottom left of the window.
A table can be visualized in more than one layout.
A layout may display fields from a table or its related fields from other tables.
A file may show data within different layouts.
Visualization of a field is independent from the storage of the contained data.
Browsing among the layouts can be done by clicking on the 'Layout:' pop-up Menu in the upper left corner.
You may browse the database by clicking on the small book pages at the top left of the window, by using the cursor to the right of the small book icon or by
entering a record number and clicking on the "Return" key.
The following information is constantly displayed on the Status toolbar (if not, select "Status Toolbar" from the "View" Menu):
Records: total number of Records in the table.
Found: total number of the subset of Records currently selected. Clicking on the green circular button will retrieve the complementary subset of currently omitted records.
Sorted: sorting status of the Records (Sorted/Unsorted).
The FileMaker Pro-based database may be used basically in these "modes":
'Browse', 'Find', and 'Preview'.
Switching among different modes can be done from the 'View' Menu or from the pop-up Menu bar at the bottom left of the window.
It allows entry, viewing, browsing,
sorting, and manipulation of data.
It may be selected from
the 'View' menu or
the pop-up mode Menu bar at the bottom left of the window.
It may be selected from
the 'View' menu or
the pop-up mode Menu bar at the bottom left of the window.
In the 'Browse' mode, the
record sets can be browsed by clicking on the small book icon (with the arrows
to move 'back' and 'forward') in the upper left corner.
Browsing among the tables can
be done by clicking on the 'Layout:' pop-up Menu in the upper
left corner.
An alternative mode for using
the database.
It allows you to search for specific content in the database fields, using any different combination of criteria
(see the 'Find mode' section below for more details).
It may be selected from
the 'View' menu,
the mode pop-up Menu bar at the bottom left of the window or
the button.
button.
The user can fill in a blank form allowing searches in specific fields.
In the "Find" mode, the small book icon in the upper left corner represents different "requests" that are made for searching the database.
In FileMaker Pro 'Find' mode, the "AND" - "OR" - "NOT" operators may be implemented in this way:
"AND" by filling criteria in different fields
located in the same "Request",
"OR" by generating additional requests
(from the "Requests" Menu) in the same query,
"NOT" by generating additional requests
(from the "Requests" Menu) and clicking on the "Omit"
button (located on the top bar in the window).
The 'Operators' pop-up Menu appears by clicking on a field while pressing the 'ctrl' key, allowing the query of:
exact matches, duplicate values, ranges, wild cards and more.
Click on the 'Perform Find' button at the top of the window to start the query.
The result of the search is the subset of the entries matching the set search criteria.
Tips:
- for an efficient record retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using the Gene_ID field instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval of genes with the same root);
- we recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol; for example using the search "=FAS" in the Gene_Symbol field will retrieve the gene FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1;
- in order to search for records with an empty field, use the "=" symbol not followed by anything in the desired field;
- in order to search for exact text at the end of the string, we recommend the use of the "*" symbol, followed by the letters; for example using the search *CAG in the Exon_Sequence field will retrieve records with exon sequence ending with "CAG".
It allows you to search for specific content in the database fields, using any different combination of criteria
(see the 'Find mode' section below for more details).
It may be selected from
the 'View' menu,
the mode pop-up Menu bar at the bottom left of the window or
the
The user can fill in a blank form allowing searches in specific fields.
In the "Find" mode, the small book icon in the upper left corner represents different "requests" that are made for searching the database.
In FileMaker Pro 'Find' mode, the "AND" - "OR" - "NOT" operators may be implemented in this way:
"AND" by filling criteria in different fields
located in the same "Request",
"OR" by generating additional requests
(from the "Requests" Menu) in the same query,
"NOT" by generating additional requests
(from the "Requests" Menu) and clicking on the "Omit"
button (located on the top bar in the window).
The 'Operators' pop-up Menu appears by clicking on a field while pressing the 'ctrl' key, allowing the query of:
exact matches, duplicate values, ranges, wild cards and more.
Click on the 'Perform Find' button at the top of the window to start the query.
The result of the search is the subset of the entries matching the set search criteria.
Tips:
- for an efficient record retrieval of unique gene/s we recommend using the Gene_ID field instead of the gene symbol (which may lead to the retrieval of genes with the same root);
- we recommend using the "=" symbol followed by the gene symbol; for example using the search "=FAS" in the Gene_Symbol field will retrieve the gene FAS and the antisense FAS-AS1;
- in order to search for records with an empty field, use the "=" symbol not followed by anything in the desired field;
- in order to search for exact text at the end of the string, we recommend the use of the "*" symbol, followed by the letters; for example using the search *CAG in the Exon_Sequence field will retrieve records with exon sequence ending with "CAG".
An alternative way of
using the database.
It visualizes a print preview of the found records.
It may be selected from
the "View" menu or
the pop-up Menu bar at the bottom left of the window.
In the "Preview" mode, the user can obtain a print preview of the data in the current table.
Browsing among the tables can be done by clicking on the 'Layout:' pop-up Menu in the upper left corner.
It visualizes a print preview of the found records.
It may be selected from
the "View" menu or
the pop-up Menu bar at the bottom left of the window.
In the "Preview" mode, the user can obtain a print preview of the data in the current table.
Browsing among the tables can be done by clicking on the 'Layout:' pop-up Menu in the upper left corner.
About
FileMaker Pro Runtime...
Information about FileMaker Pro Runtime at the core of the software.
Preferences...
Standard preferences panel; cache memory size can be set at up to 256 Mb.
Hide GeneBase
Hides all GeneBase windows.
Quit GeneBase
Closes the programme.
Information about FileMaker Pro Runtime at the core of the software.
Preferences...
Standard preferences panel; cache memory size can be set at up to 256 Mb.
Hide GeneBase
Hides all GeneBase windows.
Quit GeneBase
Closes the programme.
File
Options...
It is only possible to set the "Spelling" options.
Change Password...
There is no default password set.
Page Setup...
Standard page set up command.
Print...
Standard print command.
The appearance will match the layout currently displayed on the screen.
Import Records
This is the general "Import" function of FileMaker Pro.
Export Records...
It is only possible to set the "Spelling" options.
Change Password...
There is no default password set.
Page Setup...
Standard page set up command.
Print...
Standard print command.
The appearance will match the layout currently displayed on the screen.
Import Records
This is the general "Import" function of FileMaker Pro.
Export Records...
Export command for the found records set in a
given table.
Records are exported in their current sorting mode.
User can select fields to be exported, their relative order,
and the separation character.
Records are exported in their current sorting mode.
User can select fields to be exported, their relative order,
and the separation character.
Save/Send Records As...
Saves records to a specified Excel worksheet.
Send
Sends an intranet or internet email message (with or without a file attachment) to one or more recipients.
Email can be sent through an email application or via SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, a set of criteria for sending and receiving email).
Save a Copy as...
Save a copy of the database, compacted,
compressed, as
a clone (database structure with no record present) or as a
self-contained copy.
5.3 'Edit' Menu
(Back to Index)
Undo
Standard "Undo" command.
Redo
Standard "Redo" command.
Cut
Standard "Cut" text command.
Copy
Standard "Copy" text command.
Paste
Standard "Paste" command.
Paste Text Only
Standard "Paste" text command.
Clear
Deletes the contents of the specified field in the current record.
Select all
Selection of all text present within a selected field
(to select a field, click on the field).
Find/Replace
Utility for searching/replacing text strings within fields.
Note: Use 'Find' mode (from the "View" Menu) for full search and selection of a record set.
Spelling
Function for checking spelling of text strings within fields.
Export Field Contents...
Function for exporting the contents of the selected field to a file.
5.4 'View' Menu
(Back to Index)
Browse
Mode
Switch to the 'Browse Mode' (see "General Definitions" above).
Find Mode
Switch to the 'Find Mode' (see "General Definitions" above).
Preview Mode
Switch to the 'Preview Mode' (see "General Definitions" above).
Go to layout
A possible way to switch between different layouts.
View as Form
A possible way to individually display the current record of a found set of records.
View as List
A possible way to display all the records of a found set in the form of a list.
View as Table
A possible way to display all the records of a found set in the form of a spreadsheet-like table.
Status Toolbar
To switch on/off the "Status Toolbar": the toolbar located at the top of the programme window.
Customize Status Toolbar
To customize the "Status Toolbar" buttons.
Formatting bar
To switch on/off the "Formatting Toolbar".
Ruler
To switch on/off the text ruler of the application.
Zoom in
Used to increase layout dimensions.
Zoom out
Used to decrease layout dimensions.
Switch to the 'Browse Mode' (see "General Definitions" above).
Find Mode
Switch to the 'Find Mode' (see "General Definitions" above).
Preview Mode
Switch to the 'Preview Mode' (see "General Definitions" above).
Go to layout
A possible way to switch between different layouts.
View as Form
A possible way to individually display the current record of a found set of records.
View as List
A possible way to display all the records of a found set in the form of a list.
View as Table
A possible way to display all the records of a found set in the form of a spreadsheet-like table.
Status Toolbar
To switch on/off the "Status Toolbar": the toolbar located at the top of the programme window.
Customize Status Toolbar
To customize the "Status Toolbar" buttons.
Formatting bar
To switch on/off the "Formatting Toolbar".
Ruler
To switch on/off the text ruler of the application.
Zoom in
Used to increase layout dimensions.
Zoom out
Used to decrease layout dimensions.
5.5 'Records' Menu
(Back to Index)
New Record
Creates a new empty record in the database.
The new Record will be the latest in the current record set.
Duplicate Record
Duplicates the current record in the database.
The new Record will be the latest in the current record set.
Delete All Records
Deletes all the records in the database.
Delete Found Records...
Deletes all currently found records in the database.
Go to Record
Moves to the selected record by number, previous or next.
Refresh Window
Updates the entire contents of the database window, including any related records.
Show All Records
Shows all the records in the database.
Show Omitted Only
Shows all the records in the database not included in the current found set.
Omit Record
Removes the selected record out of the current found set, without deleting it.
Omit Multiple...
Removes more than one record, selected by numbers, out of the current found set, without deleting them.
Modify Last Find
Returns to the last performed search in order to edit it.
Saved Finds
Saves a set of search criteria.
Sort Records...
Sorts the current record set according to desired criteria.
In the Sort Records dialog box, from the left square choose the desired table fields available for sorting in the order you want them sorted and click on the "Move" button. Clicking on the "Clear" button will delete previously chosen fields. By default, the records remain sorted until you perform a find or sort records by different criteria.
This function is available also clicking on the
Unsort
Displays the current record set according to the order of creation of each record.
Replace Field Contents...
Replaces the value of a field in all sets of records found with the value specified in the current record, or by calculation.
Relookup Field Contents
This
command updates the value of a field by reading the matched
value in a related table (the relationship has been
established during database development using a 'key'
field).
Revert Record...
Restores the value of a field, discarding any change, before clicking out of that field.
5.6 'Scripts' Menu
(Back to Index)
GeneBase_Guide
The
page with the user Guide of the GeneBase software.
Import_Summary_Table_Ontology
Please see section 1.3.
Export_Selected_Records
Please see section 2.1.
Import_Exon_Intron_Sequences
Please see section 2.3.
5.7 'Help' Menu
(Back to Index)
Search
Search a 'Help' system for general commands.
Import_Summary_Table_Ontology
Please see section 1.3.
Export_Selected_Records
Please see section 2.1.
Import_Exon_Intron_Sequences
Please see section 2.3.
5.7 'Help' Menu
(Back to Index)
Search
Search a 'Help' system for general commands.
TROUBLESHOOTING (Back to Index)
Sometimes,
power failure, hardware problems, or other factors can
damage a
FileMaker Pro database file.
When the runtime application discovers a damaged file, a dialog box appears, prompting the user to contact the creator.
Even if the dialogue box does not appear, files can exhibit erratic behaviour.
If you have FileMaker Pro or FileMaker Pro Advanced installed you can recover them using the 'Recover' command.
Otherwise, to recover a damaged file:
- On Mac OS X machines, press Command + Option (cmd-alt) while double-clicking the runtime application icon. Hold the keys down until you see the 'Open Damaged File' dialogue box.
- On Windows machines, press Ctrl+Shift while double-clicking the runtime application icon. Hold the keys down until you see the Open Damaged File dialogue box.
During the recovery process, the runtime application:
1. Creates a new file;
When the runtime application discovers a damaged file, a dialog box appears, prompting the user to contact the creator.
Even if the dialogue box does not appear, files can exhibit erratic behaviour.
If you have FileMaker Pro or FileMaker Pro Advanced installed you can recover them using the 'Recover' command.
Otherwise, to recover a damaged file:
- On Mac OS X machines, press Command + Option (cmd-alt) while double-clicking the runtime application icon. Hold the keys down until you see the 'Open Damaged File' dialogue box.
- On Windows machines, press Ctrl+Shift while double-clicking the runtime application icon. Hold the keys down until you see the Open Damaged File dialogue box.
During the recovery process, the runtime application:
1. Creates a new file;
2. Renames any damaged files
by adding “Old” to the end of the
file name;
file name;
3.
Gives the repaired file the original name.